The Gift of LOVE
Finally became the POWER of LOVE
Across the WORLD...
.....the 21st Century
Despite the abundance of diamonds in certain parts of the East, surprisingly little is know about their introduction to Asia. Based on archeological research, as early as the seventh or eight century BC diamonds were mined in India. They entered China through the Western regions and were referred as "the blade that cuts jade." According to Chinese belief at the time, "Diamonds are worn by foreigners and it is said that they can avert evil airs".

China - Diamond Ring ( 265 - 316 BC ).
In 1975, at Nanking's Hsiang Shan, a group of tombs containing local aristocrats from the late Western Chin were uncovred. among the objects found was adiamond ring. The diamond, about 1 - 2mm in diameter, is in its natural crystalline structure and was mounted with the tip of the pyramid facing ourwards. The plain ring band has a square hole of about 4mm in length in which the diamond was set.
 Indonesian tradional Court Ring.
Indonesian tradional Court Ring.
This ring, dating back to the mid - 1800's, is typical of the Central Jawanese courts. It features a large, table-cut diamond set in a silver bezel. The band itself is 22K gold and was probably worn or given as a form of ornament, as the Western concept of betrothal rings did not appear in Indonesia until the mid-1900's
 Indonesian Tradional Sumatran Ring.
Indonesian Tradional Sumatran Ring.
This beautifully crafted tradional ring is from the province of Acheh in Northern Sumatra. it features three large rose-cut diamond skins set in 18K gold. The ring is around 200 years old and was probably passed on through the gernerations of a particular Sumatran noble family.
 Malaysian Studded Diamond Ring.
Malaysian Studded Diamond Ring.
This solidly crafted ring with its linear shape is studded with 7 pieces of diamond skins. The ring originated in Malaysia's Kelantan region where the vast majority of specialist craftmen were once located. This ring was ordered as one of a pair, the other with a different design. The two rings were worn on differentfingers at the same time by the owner. The ring weighs 6.9 grammes and is 2mm high.

Malaysian 'Moon And Star' Ring.
This ring of 20K yellow gold is an exquisite example of craftmanship also frm Kelantan. The ring once belonged to one of the Malaysia's royal families. Its uniqye astrological design, featuring the Moon and Star is typically in keeping with the beliefs of its Muslim owner. The ring weighs 55 grammes and stands 2mm high.
The 4C'S
Today's diamond is judged by four dintinct factors that combine in a number if ways to arrive its value. These are called the 4C's.
CARAT WEIGHT
As with all precious stones, the weight - and therefore the size-of a diamond is expressed in carats. The word carat originated in a natural unit of weight: the seed of the carob tree. Diamonds were traditionally weighed against these seeds until the system was standardised and one carat fixed at 0.2grams ( one fifth of a gram). One carat is divided into 100 "points" so that a diamond of 25 points is descibed as quarter of a carat or 0.25 carats.
CLARITY
Almost all diamonds contain minute trace of non-crystallised carbon, the element from which they were born. Most are not discernible to the naked eye require magnification to become apparent. Called inclusion, they are nature's finger print and nake every diamond unique. However, the fewer there are, the rarer the stone will be.
COLOUR
Diamonds can cover the entire spectrum of colours; the majority range from those with a barely perceptible yellow or brownish tint, up to those that are very rare and are descibed as colourless. Some even rarer stones are naturally coloured and are often refferd to as Fancies. These diamonds are only found very occasionally and come in tints such as green, pink, blue or amber.
CUT
Of all the 4C's, cut is the one most directly inflenced by man. The other three are dictated by nature. The cut or make of a diamond will dramatically influence its fire and sparkle. and it is the skill of the cutter that has most dramatically affected our perception of the diamond.

HOW A DIAMOND HANDLES LIGHT
The cut enables a diamond to make the best use of light.
1. When a diamond is cut to good proportions, light is reflected from one facet to another and then dispersed through the top of the stone.
2. If the cut of the diamond is too deep, some light escapes through the opposite side of the pavilion.
3. If the cut is too shallow, light escapes through the pavilion before it can be reflected.
DIFFERENT DIAMOND CUTS

1 . The Round Brilliant.
Throughtout history, the shape of a finished diamond has taken many provocative and seductive forms.
Such as the curvaceous Oval. The symmetrical Emerald. The delicate Pear. The bold Square. The elegant Marquise.
Diamond shapes that take the world's most treasured stone beyond the more tradional round Brilliant.
Feast your eyes on the Seductive Shape Diamonds that have captured the heartd of men and women through the ages.
Admire the fire. Thrill to their colourful history. Behold their distinctive silhouette.
Bearing in mind that diamonds come in all sizes and carat weights to suit your individual desires.
2. The Oval
The Oval shape diamond is distinctive for its feminine shape. A slightly elongated form, the Oval gives off a sparkling, "twinkling" appearance,catching and reflecting light from all directions.
The resurjence of more feminine fashions makes the Oval a natural choise for today's sophisicated women. one of the world's most famous Oval shape diamonds is the " Koh-i-Noor" from India which resides in the Crown Jewels in the Tower of London.
3. The Marquise
One of the most elegant diamond shapes is the Marquise.
The shape is oblong and characterised by pinpoint flashes of fiery brilliance that comes to a point on both ends. this shape is often used as a centre stone, mixing ovals and rounds as accent stones in contemporary mountings.
It was named after the exquisite Madame de Pompadour, renowned marquise, duchess and mistress of King Louis XV.
4. The Heart Shape
The Heart shape is one of the most distinctive shape among all the shape, because of the shape resembles heart, the place where the flower of LOVE blooms.
Rings with this diamond dignifys the most well renown Royal Engagements and Royal Weddings. It is also believed that when Heart shaped diamond is presented, the wearer will feel the electrifying love straight to the heart.
5. The Emerald Cut
One of the more dictinctive diamond shape ever, the Emerald shape diamond emphasises the transparent beauty of the stone.
rectangular in outline, its four corners and left right symmetry make to symbol of discipline and order. In 1949, King Farouk of Egypt bought the famous Jonker Diamond an exquiste example of an Emerald shape.
In 1952, he exiled and the whereabouts of this diamond remain a mystery.
6. The Pear Shape.
The Pear shape diamond is distinctive for its feminine shape. The delicay not only in the shape but also in the look. The extraordinary fire sparkling and brilliance that comes at the point.
This diamond often used as centre stone and the shoulders of the ring with small round brilliant to give supportive sparklings.
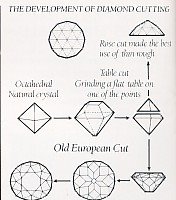
THE DEVELOPMENT OF DIAMOND CUTTING
The above illustrates the othordox cutting which known as the Old European Cut. Which did not get the real fire and brilliance until they have the following;
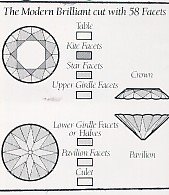 The above is the modern brilliant cut with 58 Facets, whereby, the cut never went too deep or too shallow. In these cutting the culex is carefuuly taken care to enhance the ultimate sparkle to reflect the full fire and the brilliance.
The above is the modern brilliant cut with 58 Facets, whereby, the cut never went too deep or too shallow. In these cutting the culex is carefuuly taken care to enhance the ultimate sparkle to reflect the full fire and the brilliance.
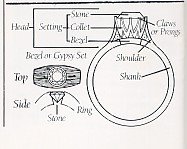
The above is the modern setting which gives exclusiveness to the wearer.

China - Diamond Ring ( 265 - 316 BC ).
In 1975, at Nanking's Hsiang Shan, a group of tombs containing local aristocrats from the late Western Chin were uncovred. among the objects found was adiamond ring. The diamond, about 1 - 2mm in diameter, is in its natural crystalline structure and was mounted with the tip of the pyramid facing ourwards. The plain ring band has a square hole of about 4mm in length in which the diamond was set.
 Indonesian tradional Court Ring.
Indonesian tradional Court Ring.This ring, dating back to the mid - 1800's, is typical of the Central Jawanese courts. It features a large, table-cut diamond set in a silver bezel. The band itself is 22K gold and was probably worn or given as a form of ornament, as the Western concept of betrothal rings did not appear in Indonesia until the mid-1900's
 Indonesian Tradional Sumatran Ring.
Indonesian Tradional Sumatran Ring. This beautifully crafted tradional ring is from the province of Acheh in Northern Sumatra. it features three large rose-cut diamond skins set in 18K gold. The ring is around 200 years old and was probably passed on through the gernerations of a particular Sumatran noble family.
 Malaysian Studded Diamond Ring.
Malaysian Studded Diamond Ring.This solidly crafted ring with its linear shape is studded with 7 pieces of diamond skins. The ring originated in Malaysia's Kelantan region where the vast majority of specialist craftmen were once located. This ring was ordered as one of a pair, the other with a different design. The two rings were worn on differentfingers at the same time by the owner. The ring weighs 6.9 grammes and is 2mm high.

Malaysian 'Moon And Star' Ring.
This ring of 20K yellow gold is an exquisite example of craftmanship also frm Kelantan. The ring once belonged to one of the Malaysia's royal families. Its uniqye astrological design, featuring the Moon and Star is typically in keeping with the beliefs of its Muslim owner. The ring weighs 55 grammes and stands 2mm high.
The 4C'S
Today's diamond is judged by four dintinct factors that combine in a number if ways to arrive its value. These are called the 4C's.
CARAT WEIGHT
As with all precious stones, the weight - and therefore the size-of a diamond is expressed in carats. The word carat originated in a natural unit of weight: the seed of the carob tree. Diamonds were traditionally weighed against these seeds until the system was standardised and one carat fixed at 0.2grams ( one fifth of a gram). One carat is divided into 100 "points" so that a diamond of 25 points is descibed as quarter of a carat or 0.25 carats.
CLARITY
Almost all diamonds contain minute trace of non-crystallised carbon, the element from which they were born. Most are not discernible to the naked eye require magnification to become apparent. Called inclusion, they are nature's finger print and nake every diamond unique. However, the fewer there are, the rarer the stone will be.
COLOUR
Diamonds can cover the entire spectrum of colours; the majority range from those with a barely perceptible yellow or brownish tint, up to those that are very rare and are descibed as colourless. Some even rarer stones are naturally coloured and are often refferd to as Fancies. These diamonds are only found very occasionally and come in tints such as green, pink, blue or amber.
CUT
Of all the 4C's, cut is the one most directly inflenced by man. The other three are dictated by nature. The cut or make of a diamond will dramatically influence its fire and sparkle. and it is the skill of the cutter that has most dramatically affected our perception of the diamond.

HOW A DIAMOND HANDLES LIGHT
The cut enables a diamond to make the best use of light.
1. When a diamond is cut to good proportions, light is reflected from one facet to another and then dispersed through the top of the stone.
2. If the cut of the diamond is too deep, some light escapes through the opposite side of the pavilion.
3. If the cut is too shallow, light escapes through the pavilion before it can be reflected.
DIFFERENT DIAMOND CUTS

1 . The Round Brilliant.
Throughtout history, the shape of a finished diamond has taken many provocative and seductive forms.
Such as the curvaceous Oval. The symmetrical Emerald. The delicate Pear. The bold Square. The elegant Marquise.
Diamond shapes that take the world's most treasured stone beyond the more tradional round Brilliant.
Feast your eyes on the Seductive Shape Diamonds that have captured the heartd of men and women through the ages.
Admire the fire. Thrill to their colourful history. Behold their distinctive silhouette.
Bearing in mind that diamonds come in all sizes and carat weights to suit your individual desires.
2. The Oval
The Oval shape diamond is distinctive for its feminine shape. A slightly elongated form, the Oval gives off a sparkling, "twinkling" appearance,catching and reflecting light from all directions.
The resurjence of more feminine fashions makes the Oval a natural choise for today's sophisicated women. one of the world's most famous Oval shape diamonds is the " Koh-i-Noor" from India which resides in the Crown Jewels in the Tower of London.
3. The Marquise
One of the most elegant diamond shapes is the Marquise.
The shape is oblong and characterised by pinpoint flashes of fiery brilliance that comes to a point on both ends. this shape is often used as a centre stone, mixing ovals and rounds as accent stones in contemporary mountings.
It was named after the exquisite Madame de Pompadour, renowned marquise, duchess and mistress of King Louis XV.
4. The Heart Shape
The Heart shape is one of the most distinctive shape among all the shape, because of the shape resembles heart, the place where the flower of LOVE blooms.
Rings with this diamond dignifys the most well renown Royal Engagements and Royal Weddings. It is also believed that when Heart shaped diamond is presented, the wearer will feel the electrifying love straight to the heart.
5. The Emerald Cut
One of the more dictinctive diamond shape ever, the Emerald shape diamond emphasises the transparent beauty of the stone.
rectangular in outline, its four corners and left right symmetry make to symbol of discipline and order. In 1949, King Farouk of Egypt bought the famous Jonker Diamond an exquiste example of an Emerald shape.
In 1952, he exiled and the whereabouts of this diamond remain a mystery.
6. The Pear Shape.
The Pear shape diamond is distinctive for its feminine shape. The delicay not only in the shape but also in the look. The extraordinary fire sparkling and brilliance that comes at the point.
This diamond often used as centre stone and the shoulders of the ring with small round brilliant to give supportive sparklings.

THE DEVELOPMENT OF DIAMOND CUTTING
The above illustrates the othordox cutting which known as the Old European Cut. Which did not get the real fire and brilliance until they have the following;
 The above is the modern brilliant cut with 58 Facets, whereby, the cut never went too deep or too shallow. In these cutting the culex is carefuuly taken care to enhance the ultimate sparkle to reflect the full fire and the brilliance.
The above is the modern brilliant cut with 58 Facets, whereby, the cut never went too deep or too shallow. In these cutting the culex is carefuuly taken care to enhance the ultimate sparkle to reflect the full fire and the brilliance.
The above is the modern setting which gives exclusiveness to the wearer.


0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home